二叉树
1. 递归的逻辑
- 明确函数的「定义」是什么,然后相信这个定义,利用这个定义推导最终结果,绝不要跳入递归的细节。
- 以内部函数调用为分界,上部分是入栈,下部分是出栈
// 定义:count(root) 返回以 root 为根的树有多少节点
int count(TreeNode root) {
// base case
if (root == null) return 0;
// 自己加上子树的节点数就是整棵树的节点数
return 1 + count(root.left) + count(root.right);
}
2. 二叉树的操作逻辑
先搞清楚当前 root 节点「该做什么」(重点)以及「什么时候做」(前,中,后),然后根据函数定义递归调用子节点。
/* 二叉树遍历框架 */
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
// 前序遍历
traverse(root.left)
// 中序遍历
traverse(root.right)
// 后序遍历
}
3. 二叉树前,中,后序列化与反序列化
- 序列化储存形式:
12#4 3,#表示空节点 - 改变「解析」和「序列化」位置,可以分别实现前,中,后。
- 深度优先搜索
struct Node{
int value;
Node* left;
Node* right;
Node(){
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
~Node(){
if (left != nullptr)
{
delete left;
}
if (right != nullptr)
{
delete right;
}
}
};
class BinaryTree{
private:
const string nullStr = "#";
public:
Node* deserialize(queue<string> &nodes){
// 读取一个节点
string str = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
// 到头了
if (str == nullStr)
{
return nullptr;
}
// 解析
Node* node = new Node();
node->value = stoi(str);
// 解析左右节点
node->left = deserialize(nodes);
node->right = deserialize(nodes);
return node;
}
string serialize(Node* root){
// 节点到头了
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullStr;
}
// 序列化
string str = to_string(root->value);
// 序列化左右
str = str + serialize(root->left);
str = str + serialize(root->right);
return str;
}
};
4. 二叉树层级遍历的序列化与反序列化
- 序列化: 递归的作用,1)将父节点输出;2)子节点入队;3)当父节点出队
string serializeProcess(Node* root){
if (nodeQueue.empty())
{
return "";
}
// 搜索到头
string str = "";
if (root == nullptr)
{
str = nullnode;
}else{
str = to_string(root->value);
// 子节点入队
nodeQueue.push(root->left);
nodeQueue.push(root->right);
}
// 将当前节点弹出
nodeQueue.pop();
str = str + serializeProcess(nodeQueue.front());
return str;
}
string serialize(Node* root){
while (!nodeQueue.empty())
{
nodeQueue.pop();
}
// 初始化队列
nodeQueue.push(root);
return serializeProcess(nodeQueue.front());
}
- 反序列化: 递归的作用,1)父节点出队;2)解析左右子节点;3)子节点入队
void deserializeProcess(queue<string>& nodes){
if(nodes.empty()){
return;
}
// 取出一个父类
Node* parent = nodeQueue.front();
nodeQueue.pop();
string str = "";
Node* node = nullptr;
// 取出左子节点
str = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
if (str == nullnode)
{
node = nullptr;
}else{
node = new Node();
node->value = stoi(str);
nodeQueue.push(node);
}
parent->left = node;
// 取出右子节点
str = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
if (str == nullnode)
{
node = nullptr;
}else{
node = new Node();
node->value = stoi(str);
nodeQueue.push(node);
}
parent->right = node;
deserializeProcess(nodes);
}
Node* deserialize(queue<string>& nodes){
while (!nodeQueue.empty())
{
nodeQueue.pop();
}
if (nodes.front() == nullnode)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* root = new Node();
root->value = stoi(nodes.front());
nodes.pop();
nodeQueue.push(root);
deserializeProcess(nodes);
return root;
}
5. 翻转二叉树
void invertTree(Node * root){
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
// 交换节点
Node* temp = root->left;
root->left = root->right;
root->right = temp;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
}
6. 连通完全二叉树一层的节点
// 主函数
Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) return null;
connectTwoNode(root.left, root.right);
return root;
}
// 辅助函数
void connectTwoNode(Node node1, Node node2) {
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
return;
}
/**** 前序遍历位置 ****/
// 将传入的两个节点连接
node1.next = node2;
// 连接相同父节点的两个子节点
connectTwoNode(node1.left, node1.right);
connectTwoNode(node2.left, node2.right);
// 连接跨越父节点的两个子节点
connectTwoNode(node1.right, node2.left);
}
[!tip|style:flat] 「将每两个相邻节点都连接起来」
7. 将二叉树变链表
- 将 root 的左子树和右子树拉平
- 将 root 的右子树接到左子树下方
- 将整个左子树作为右子树。
// 定义:将以 root 为根的树拉平为链表
void flatten(TreeNode root) {
// base case
if (root == null) return;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(root.right);
/**** 后序遍历位置 ****/
// 1、左右子树已经被拉平成一条链表
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
// 2、将左子树作为右子树
root.left = null;
root.right = left;
// 3、将原先的右子树接到当前右子树的末端
TreeNode p = root;
while (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
p.right = right;
}
8. 构造最大二叉树
- 左右拆分找节点
Node* constructMaximumBinaryTree(int* nums,int left,int right){
if(left > right){
return nullptr;
}
// 找最大值
int max = nums[left];
int maxIndex = left;
for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++)
{
if (max < nums[i])
{
max = nums[i];
maxIndex = i;
}
}
// 生成节点
Node* node = new Node();
node->value = max;
node->left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums,left,maxIndex - 1);
node->right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums,maxIndex + 1,right);
return node;
}
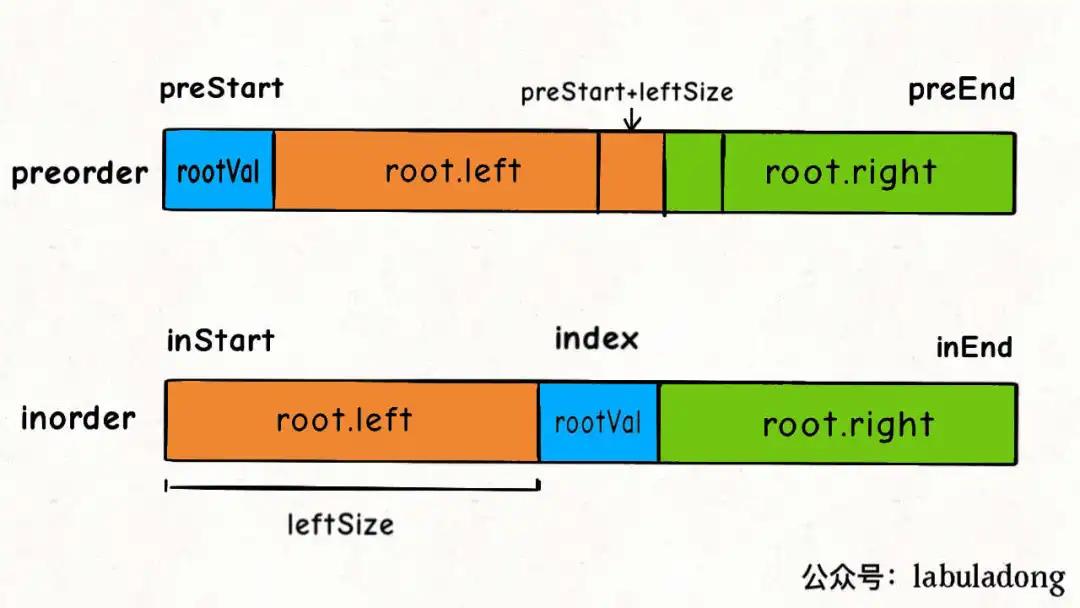
9. 通过「前序和中序」遍历结果构造二叉树
- 递归创建处理
root节点 - 在中序中,找
root节点位置 - 左右拆分,进行递归。 重点为
preorder,inorder如何拆两半 。 - 两种序列,传参时,不能搞错了。
Node* fromPreIn(int* preorder,int preL,int preR,int* inorder,int inL,int inR){
if (preL > preR || inL > inR)
{
return nullptr;
}
// 根节点
Node* root = new Node();
root->value = preorder[preL];
// 中序中,找root所在位置
int index = 0;
for ( index = inL; index <= inR; index++)
{
if(inorder[index] == root->value){
break;
}
}
// 两个子节点
root->left = fromPreIn(preorder,preL + 1,preL + (index - inL),
inorder,inL,index - 1);
root->right = fromPreIn(preorder,preL + (index - inL) + 1,preR,
inorder,index + 1,inR);
return root;
}
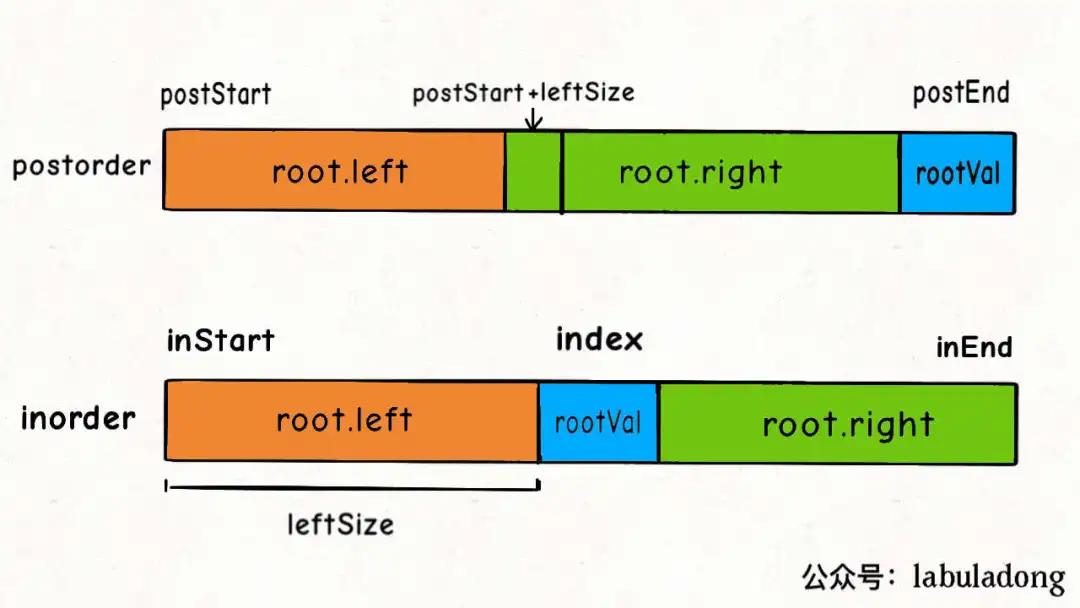
10. 通过「中序和后序」遍历结果构造二叉树
[!note|style:flat] 注意:
postR - 1
root->left = fromPostIn(postorder,postL,postL + interval - 1,
inorder,inL,index - 1);
root->right = fromPostIn(postorder,postL+interval,postR - 1,
inorder,index+1,inR);